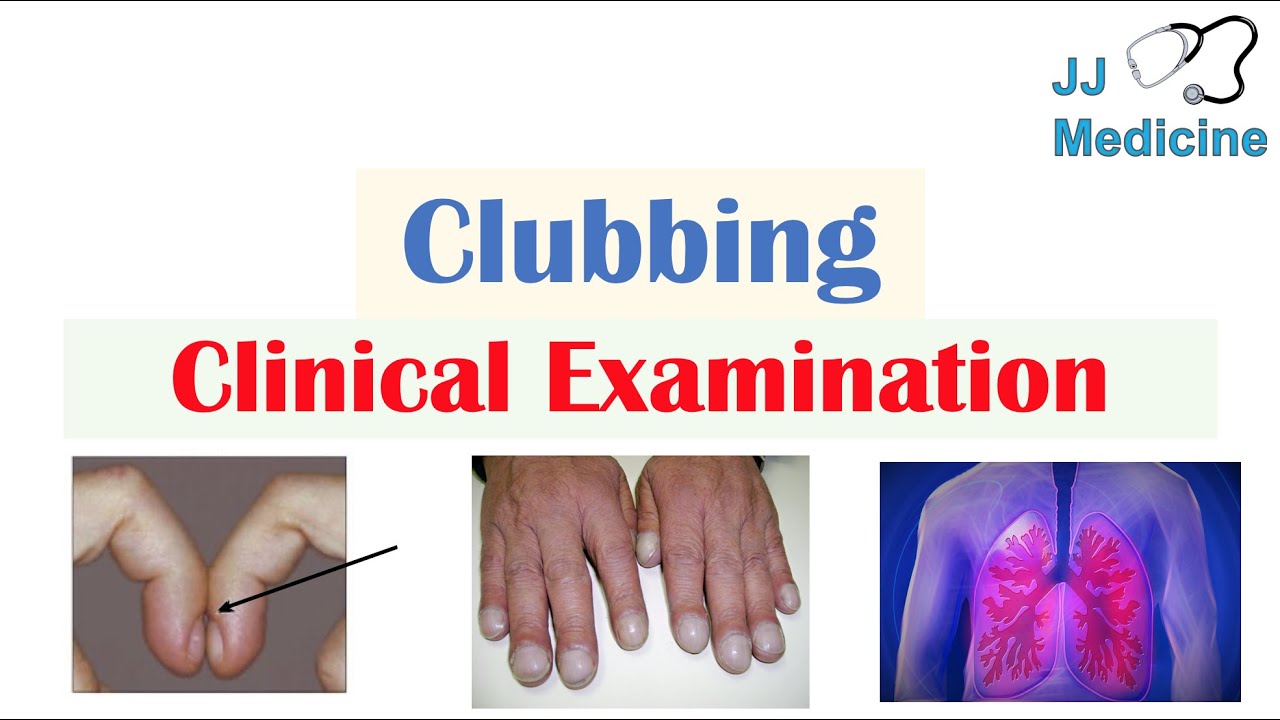
What is clubitis disease?
Clubbing is a condition in which the tips of the fingers or toes become wider and rounder than normal. It can be caused by a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Clubbing is often diagnosed based on a physical exam. Your doctor may also order tests to determine the underlying cause of the clubbing.
Treatment for clubbing depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, treating the underlying condition may resolve the clubbing. In other cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the clubbing.
Clubbing
Clubbing is a condition in which the tips of the fingers or toes become wider and rounder than normal. It can be caused by a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
- Definition: Clubbing is a condition that affects the shape of the fingers and toes.
- Causes: Clubbing can be caused by a variety of underlying medical conditions.
- Symptoms: The primary symptom of clubbing is wider and rounder fingertips or toenails.
- Diagnosis: Clubbing is often diagnosed based on a physical exam.
- Treatment: Treatment for clubbing depends on the underlying cause.
- Outlook: The outlook for clubbing depends on the underlying cause.
Clubbing can be a sign of a serious underlying medical condition. If you notice that your fingers or toes are becoming wider and rounder, it is important to see your doctor to rule out any underlying health problems.
1. Definition
Clubbing is a condition that can affect the shape of the fingers and toes, causing them to become wider and rounder than normal. It is often a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as heart disease, lung disease, or liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Understanding the definition of clubbing is important for recognizing and diagnosing the condition. It is a key component of clubitis disease pictures, which are used to assess the severity of clubbing and to track its progression over time.
By understanding the definition of clubbing and its connection to clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage the condition, leading to improved patient outcomes.
2. Causes
Clubbing is a condition that can affect the shape of the fingers and toes, causing them to become wider and rounder than normal. It is often a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as heart disease, lung disease, or liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Clubitis disease pictures are used to assess the severity of clubbing and to track its progression over time. By understanding the causes of clubbing, healthcare professionals can better interpret clubitis disease pictures and make more accurate diagnoses.
- Cardiovascular disease: Clubbing is a common sign of congenital heart disease, which is a birth defect that affects the structure of the heart. Clubbing can also be a sign of acquired heart disease, such as cardiomyopathy or valvular heart disease.
- Pulmonary disease: Clubbing is a common sign of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage. Clubbing can also be a sign of other lung diseases, such as interstitial lung disease or cystic fibrosis.
- Gastrointestinal disease: Clubbing is a common sign of liver disease, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis. Clubbing can also be a sign of other gastrointestinal diseases, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Cancer: Clubbing is a common sign of lung cancer, but it can also be a sign of other types of cancer, such as esophageal cancer or mesothelioma.
By understanding the causes of clubbing and their connection to clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage the condition, leading to improved patient outcomes.
3. Symptoms
Clubbing is a condition that can affect the shape of the fingers and toes, causing them to become wider and rounder than normal. It is often a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as heart disease, lung disease, or liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Clubitis disease pictures are used to assess the severity of clubbing and to track its progression over time. By understanding the symptoms of clubbing and their connection to clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage the condition, leading to improved patient outcomes.
- Visual Assessment: Clubitis disease pictures provide a visual representation of the fingers and toes, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the severity of clubbing. The pictures can be used to track changes in the shape and size of the fingers and toes over time.
- Diagnostic Tool: Clubitis disease pictures can be used as a diagnostic tool to help identify the underlying cause of clubbing. The pictures can help healthcare professionals rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms, such as edema or infection.
- Monitoring Progression: Clubitis disease pictures can be used to monitor the progression of clubbing over time. The pictures can help healthcare professionals track the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as necessary.
- Patient Education: Clubitis disease pictures can be used to educate patients about clubbing and its potential causes. The pictures can help patients understand the condition and its implications for their health.
By understanding the connection between the symptoms of clubbing and clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage the condition, leading to improved patient outcomes.
4. Diagnosis
Clubbing is a condition that can affect the shape of the fingers and toes, causing them to become wider and rounder than normal. It is often a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as heart disease, lung disease, or liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Clubitis disease pictures are used to assess the severity of clubbing and to track its progression over time. By understanding the connection between the diagnosis of clubbing and clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage the condition, leading to improved patient outcomes.
The physical exam is an important part of the diagnostic process for clubbing. During the physical exam, the doctor will look for signs of clubbing, such as wider and rounder fingertips or toenails. The doctor may also order tests to determine the underlying cause of the clubbing.
Clubitis disease pictures can be used to confirm the diagnosis of clubbing and to track its progression over time. The pictures can help healthcare professionals rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms, such as edema or infection.
By understanding the connection between the diagnosis of clubbing and clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage the condition, leading to improved patient outcomes.
5. Treatment
Clubbing is a condition that can affect the shape of the fingers and toes, causing them to become wider and rounder than normal. It is often a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as heart disease, lung disease, or liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Clubitis disease pictures are used to assess the severity of clubbing and to track its progression over time. By understanding the connection between the treatment of clubbing and clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better manage the condition and improve patient outcomes.
- Diagnosis: Clubitis disease pictures can be used to help diagnose the underlying cause of clubbing. The pictures can help healthcare professionals rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms, such as edema or infection.
- Monitoring: Clubitis disease pictures can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for clubbing. The pictures can help healthcare professionals track changes in the shape and size of the fingers and toes over time.
- Treatment: Clubitis disease pictures can be used to guide treatment decisions for clubbing. The pictures can help healthcare professionals determine the best course of treatment for the underlying medical condition that is causing the clubbing.
By understanding the connection between the treatment of clubbing and clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better manage the condition and improve patient outcomes.
6. Outlook
The outlook for clubbing depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying cause is treated successfully, the clubbing may resolve. However, if the underlying cause is not treated, the clubbing may persist or even worsen.
Clubitis disease pictures are used to assess the severity of clubbing and to track its progression over time. By understanding the connection between the outlook for clubbing and clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better manage the condition and improve patient outcomes.
For example, if a patient has clubbing and the clubitis disease pictures show that the clubbing is worsening, this may indicate that the underlying cause of the clubbing is not being treated effectively. In this case, the healthcare professional may need to adjust the treatment plan to improve the patient's outlook.
By understanding the connection between the outlook for clubbing and clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better manage the condition and improve patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions about Clubbing
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions about clubbing using a serious tone and informative style, excluding first and second-person pronouns and AI-style formalities.
Question 1: What is clubbing?
Answer: Clubbing is a condition that affects the shape of the fingers and toes, causing them to become wider and rounder than normal. It is often a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as heart disease, lung disease, or liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Question 2: What causes clubbing?
Answer: Clubbing can be caused by a variety of underlying medical conditions. Some of the most common causes include heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease. In some cases, clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Question 3: How is clubbing diagnosed?
Answer: Clubbing is often diagnosed based on a physical exam. Your doctor will look for signs of clubbing, such as wider and rounder fingertips or toenails. Your doctor may also order tests to determine the underlying cause of the clubbing.
Question 4: How is clubbing treated?
Answer: Treatment for clubbing depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying cause is treated successfully, the clubbing may resolve. However, if the underlying cause is not treated, the clubbing may persist or even worsen.
Question 5: What is the outlook for clubbing?
Answer: The outlook for clubbing depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying cause is treated successfully, the clubbing may resolve. However, if the underlying cause is not treated, the clubbing may persist or even worsen.
Summary: Clubbing is a condition that affects the shape of the fingers and toes. It can be caused by a variety of underlying medical conditions, and it can be a sign of certain types of cancer. The outlook for clubbing depends on the underlying cause.
Transition: For more information about clubbing, please consult your doctor or other healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Clubbing is a condition that can affect the shape of the fingers and toes, causing them to become wider and rounder than normal. It is often a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as heart disease, lung disease, or liver disease. Clubbing can also be a sign of certain types of cancer.
Clubitis disease pictures are used to assess the severity of clubbing and to track its progression over time. By understanding the connection between clubbing and clubitis disease pictures, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage the condition, leading to improved patient outcomes.
If you notice that your fingers or toes are becoming wider and rounder, it is important to see your doctor to rule out any underlying health problems.
Article Recommendations
- Craig Jones Bjj Record A Deep Dive Into The Acclaimed Brazilian Jiujitsu Black Belts Achievements
- Pistol Pete Osu The Legacy Of A Basketball Legend
- Lorenzo Zurzolo Wife A Deep Dive Into His Personal Life And Relationship Journey