What are clubitis syndrome symptoms?
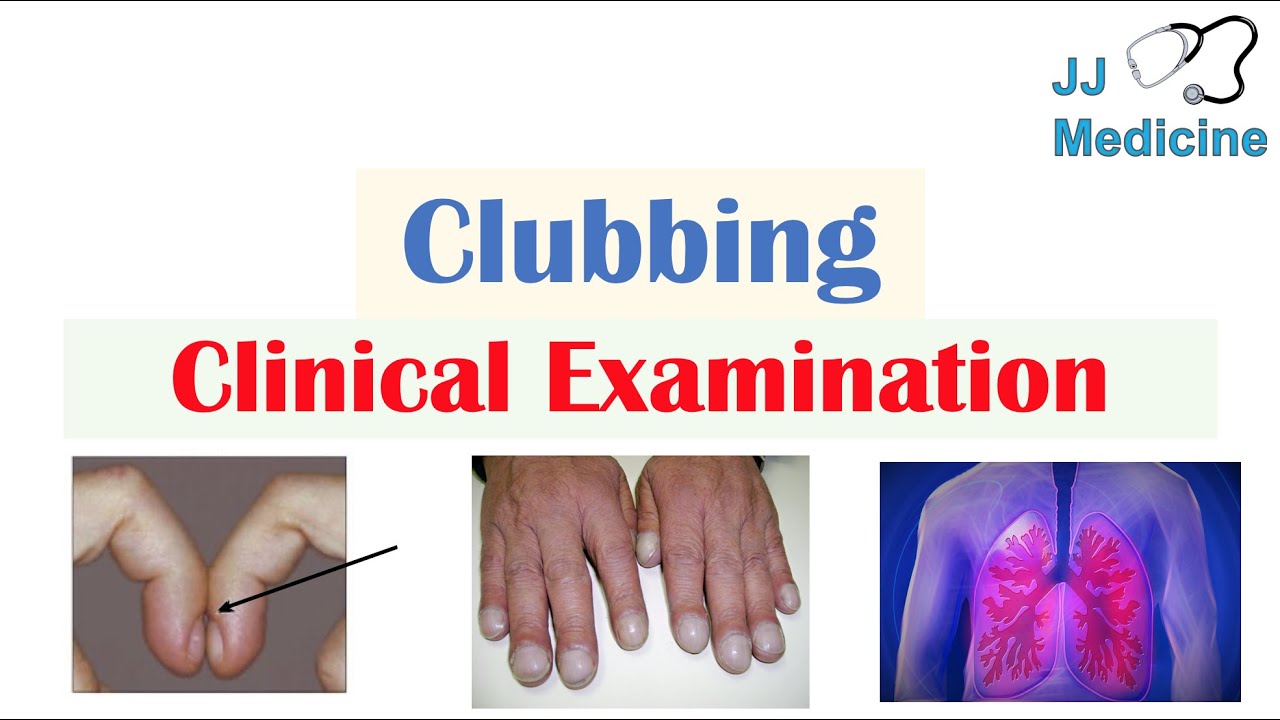
Clubbing, or clubbing of the fingers and toes, is a condition in which the tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder, and the nails become thicker and more curved. It can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
The most common symptom of clubbing is a change in the shape of the fingers and toes. The tips of the fingers and toes may become wider and rounder, and the nails may become thicker and more curved. Other symptoms of clubbing can include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Chest pain
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
Clubbing can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions. The most common cause of clubbing is heart disease. Other causes of clubbing can include:
- Lung disease
- Liver disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Certain medications
If you have clubbing, it is important to see your doctor to determine the underlying cause. Treatment for clubbing will depend on the underlying cause.
clubitis syndrome symptoms
Clubbing, or clubbing of the fingers and toes, is a condition in which the tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder, and the nails become thicker and more curved. It can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
- Shape: The tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder.
- Nails: The nails become thicker and more curved.
- Underlying conditions: Clubbing can be a sign of heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
- Symptoms: Other symptoms of clubbing can include shortness of breath, fatigue, weight loss, chest pain, and swelling in the legs or ankles.
- Causes: The most common cause of clubbing is heart disease. Other causes can include lung disease, liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain medications.
- Treatment: Treatment for clubbing will depend on the underlying cause.
Clubbing can be a serious condition, so it is important to see your doctor if you have any of the symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve the outcome.
1. Shape
The shape of the fingers and toes is one of the most noticeable symptoms of clubbing. The tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder, and the nails become thicker and more curved. This change in shape is caused by a build-up of tissue in the fingers and toes. The tissue build-up can be caused by a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
- Cardiovascular disease: Clubbing is a common sign of congenital heart disease, which is a birth defect that affects the structure of the heart. Clubbing can also be a sign of acquired heart disease, which is a condition that develops later in life.
- Lung disease: Clubbing is a common sign of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage. Clubbing can also be a sign of other lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and lung cancer.
- Liver disease: Clubbing is a common sign of cirrhosis, which is a chronic liver disease that causes scarring of the liver. Clubbing can also be a sign of other liver diseases, such as hepatitis and liver cancer.
- Other conditions: Clubbing can also be a sign of certain other medical conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease, certain medications, and certain infections.
Clubbing can be a serious condition, so it is important to see your doctor if you have any of the symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve the outcome.
2. Nails
Thickening and curving of the nails is a common symptom of clubbing. Clubbing is a condition in which the tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder, and the nails become thicker and more curved. It can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
- Cardiovascular disease: Clubbing is a common sign of congenital heart disease, which is a birth defect that affects the structure of the heart. Clubbing can also be a sign of acquired heart disease, which is a condition that develops later in life.
- Lung disease: Clubbing is a common sign of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage. Clubbing can also be a sign of other lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and lung cancer.
- Liver disease: Clubbing is a common sign of cirrhosis, which is a chronic liver disease that causes scarring of the liver. Clubbing can also be a sign of other liver diseases, such as hepatitis and liver cancer.
- Other conditions: Clubbing can also be a sign of certain other medical conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease, certain medications, and certain infections.
The thickening and curving of the nails in clubbing is caused by a build-up of tissue in the fingers and toes. This tissue build-up can be caused by a variety of underlying medical conditions. It is important to see a doctor if you have any of the symptoms of clubbing, as early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve the outcome.
3. Underlying conditions
Clubbing is a condition in which the tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder, and the nails become thicker and more curved. It can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
The connection between clubbing and underlying medical conditions is important because it can help doctors to diagnose and treat the underlying condition. For example, if a doctor sees a patient with clubbing, they may order tests to check for heart disease, lung disease, or liver disease. Early diagnosis and treatment of the underlying condition can help to improve the outcome for the patient.
In some cases, clubbing can be a sign of a serious medical condition, such as congenital heart disease or lung cancer. In these cases, early diagnosis and treatment is essential to improve the patient's chances of survival.
It is important to note that not everyone with clubbing has an underlying medical condition. However, if you have clubbing, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
4. Symptoms
In addition to the characteristic changes in the shape of the fingers and toes, clubbing can also be accompanied by a range of other symptoms. These symptoms can include shortness of breath, fatigue, weight loss, chest pain, and swelling in the legs or ankles.
- Shortness of breath is a common symptom of clubbing, especially if the underlying cause is a lung condition. This is because clubbing can lead to changes in the shape of the lungs, which can make it more difficult to breathe.
- Fatigue is another common symptom of clubbing. This is because the underlying medical condition can lead to a decrease in the body's oxygen levels, which can make people feel tired and weak.
- Weight loss is a common symptom of clubbing, especially if the underlying cause is a chronic condition, such as heart disease or lung disease. This is because these conditions can lead to a decrease in appetite and an increase in metabolism.
- Chest pain is a common symptom of clubbing, especially if the underlying cause is a heart condition. This is because clubbing can lead to changes in the shape of the heart, which can put pressure on the chest and cause pain.
- Swelling in the legs or ankles is a common symptom of clubbing, especially if the underlying cause is a liver condition. This is because clubbing can lead to changes in the shape of the liver, which can block the flow of blood and cause swelling in the legs and ankles.
It is important to note that not everyone with clubbing will experience all of these symptoms. However, if you have clubbing and are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
5. Causes
Clubbing is a condition in which the tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder, and the nails become thicker and more curved. It can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
- Heart disease is the most common cause of clubbing. Clubbing can occur in people with congenital heart disease, which is a birth defect that affects the structure of the heart. Clubbing can also occur in people with acquired heart disease, which is a condition that develops later in life.
- Lung disease is another common cause of clubbing. Clubbing can occur in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage. Clubbing can also occur in people with other lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and lung cancer.
- Liver disease can also cause clubbing. Clubbing can occur in people with cirrhosis, which is a chronic liver disease that causes scarring of the liver. Clubbing can also occur in people with other liver diseases, such as hepatitis and liver cancer.
- Inflammatory bowel disease can also cause clubbing. Clubbing can occur in people with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which are two types of inflammatory bowel disease.
- Certain medications can also cause clubbing. Clubbing can occur in people who take certain medications for heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
It is important to note that not everyone with clubbing has an underlying medical condition. However, if you have clubbing, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
6. Treatment
Clubbing is a condition in which the tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder, and the nails become thicker and more curved. It can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
The treatment for clubbing will depend on the underlying cause. For example, if the clubbing is caused by heart disease, the treatment will focus on treating the heart disease. If the clubbing is caused by lung disease, the treatment will focus on treating the lung disease. If the clubbing is caused by liver disease, the treatment will focus on treating the liver disease.
In some cases, the clubbing may improve or even go away once the underlying medical condition is treated. However, in other cases, the clubbing may be permanent. It is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and to discuss the treatment options.
FAQs about clubbing
Clubbing, or clubbing of the fingers and toes, is a condition in which the tips of the fingers and toes become wider and rounder, and the nails become thicker and more curved. It can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions, including heart disease, lung disease, and liver disease.
Question 1: What are the symptoms of clubbing?
Answer: The most common symptom of clubbing is a change in the shape of the fingers and toes. The tips of the fingers and toes may become wider and rounder, and the nails may become thicker and more curved. Other symptoms of clubbing can include shortness of breath, fatigue, weight loss, chest pain, and swelling in the legs or ankles.
Question 2: What causes clubbing?
Answer: The most common cause of clubbing is heart disease. Other causes can include lung disease, liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain medications.
Question 3: How is clubbing treated?
Answer: The treatment for clubbing will depend on the underlying cause. For example, if the clubbing is caused by heart disease, the treatment will focus on treating the heart disease. If the clubbing is caused by lung disease, the treatment will focus on treating the lung disease. If the clubbing is caused by liver disease, the treatment will focus on treating the liver disease.
Question 4: Can clubbing be prevented?
Answer: There is no sure way to prevent clubbing. However, early diagnosis and treatment of the underlying medical condition can help to prevent the clubbing from getting worse.
Question 5: What is the prognosis for clubbing?
Answer: The prognosis for clubbing depends on the underlying medical condition. If the underlying medical condition is treated early, the clubbing may improve or even go away. However, in some cases, the clubbing may be permanent.
If you have any of the symptoms of clubbing, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and to discuss the treatment options.
Summary: Clubbing is a condition that can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions. The most common cause of clubbing is heart disease. Other causes can include lung disease, liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain medications. The treatment for clubbing will depend on the underlying cause.
Transition to the next article section: If you have any of the symptoms of clubbing, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and to discuss the treatment options.
Conclusion
Clubbing is a condition that can be a sign of a variety of underlying medical conditions. The most common cause of clubbing is heart disease. Other causes can include lung disease, liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain medications. The treatment for clubbing will depend on the underlying cause.
If you have any of the symptoms of clubbing, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and to discuss the treatment options. Early diagnosis and treatment of the underlying medical condition can help to prevent the clubbing from getting worse.
Article Recommendations
- Kyndra Alyse Mayo A Rising Star In The Digital Space
- Unveiling The Wealth And Legacy Of Joan And Paul Rubschlager
- Pebbles Net Worth A Comprehensive Look At The Life And Wealth Of A Music Icon